Quality control (QC) and quality assurance (QA) are fundamental components of a robust quality management system in the construction industry. Effective quality management encompasses quality planning, assurance, and control—ensuring safety, durability, and compliance with industry regulations at both company and project levels.
Studies emphasize the financial impact of poor-quality management. According to the Construction Industry Institute (CII), inadequate quality practices can result in 10–15% cost overruns due to rework, delays, and material waste. Similarly, Juran’s Quality Handbook highlights that the cost of poor quality—including rework, scrap, and delays—typically accounts for 15–20% of total project expenses in construction and manufacturing. However, organizations are making progress. Since 2013, the amount of money wasted due to poor project performance has decreased by 27%, with only 9.9% of every dollar invested being lost compared to 13.5% a decade ago.
In a rapidly growing market like the United Arab Emirates (UAE), where the construction industry is projected to reach approximately AED 331.8432 million by 2027, maintaining high-quality standards is essential. With stringent QA/QC regulations, including Dubai Municipality’s Building Code and sustainability-driven initiatives, the UAE continues to set benchmarks for efficiency, innovation, and excellence in construction.
As a leading industry player, Engineering Contracting Company (ECC) upholds these standards by integrating rigorous QA/QC protocols, adopting cutting-edge technologies, and ensuring compliance with international best practices across all its projects.
ECC’s Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) Framework
ECC’s Quality Management System complies with ISO 9001:2015(Quality Management Systems-Requirements). To ensure rigorous quality control and continuous improvement across its operations, ECC implements the following QA/QC processes:
1. Work Inspection Process
A systematic process to verify that construction activities comply with approved drawings, specifications, and project requirements.
- a. Inspections are conducted at various stages: pre-execution, during execution, and post-execution.
- b. Inspection Test Plans (ITPs) outline critical checkpoints and acceptance criteria.
- c. Hold points require approval before progressing to the next stage.
- d. Conducted by site engineers, quality inspectors, and third-party auditors when necessary.
2. Material Inspection Process
Ensures that all materials used meet quality standards and project specifications.
- a. Includes checking supplier compliance, conducting visual inspections, and verifying test certificates.
- b. Material approval requests (MAR) are submitted before procurement.
- c. On-site sampling and testing are carried out as per regulatory standards.
- d. Non-conforming materials are quarantined and returned to suppliers.
3. Non-Conformance Control
A structured approach to managing deviations from quality requirements.
- a. Non-Conformance Reports (NCRs) are raised for defective work or materials.
- b. Root cause analysis is conducted to identify the issue source.
- c. Corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) are implemented to prevent recurrence.
- d. NCR closures require validation through re-inspections.
4. Procedure Briefing
Ensures that workforce and stakeholders understand the procedures relevant to their tasks.
- a. Conducted before executing critical tasks or implementing new processes.
- b. Covers work methodologies, safety requirements, and quality expectations.
- c. Led by quality engineers or supervisors, with documentation of attendance and briefing content.
5. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Measurement metrics to track quality performance and identify improvement areas.
- a. Common KPIs include defect rates, NCR resolution time, audit compliance scores, and supplier quality performance.
- b. Data is collected regularly and analyzed for trend identification.
- c. Findings are shared with management and stakeholders for corrective actions.
6. Quality Site Induction
A mandatory training session for all personnel before commencing work on-site.
- a. Covers project-specific quality requirements, policies, and expectations.
- b. Includes briefing on defect prevention, reporting procedures, and inspection protocols.
- c. Ensures alignment with corporate and project quality objectives.
7. Quality Alert
A proactive mechanism to raise awareness of quality issues and prevent recurrence.
- a. Issued when critical quality issues or repeated defects are identified.
- b. Communicated through email, notice boards, and toolbox talks.
- c. Includes recommended corrective actions and preventive measures.
8. Quality Walkthrough
Regular site visits to assess quality performance and identify potential issues.
- a. Conducted by quality engineers, site managers, and senior leadership.
- b. Focuses on work practices, material storage, and adherence to quality plans.
- c. Immediate feedback is provided, and necessary actions are documented.
9. Lessons Learned
A structured review process to capture and share knowledge gained from past projects.
- a. Conducted at key milestones and project completion.
- b. Involves stakeholders from different disciplines to discuss challenges and improvements.
- c. Documented in a centralized knowledge base for future reference.
10. Supplier Factory Visits
Ensures that suppliers maintain required quality standards before material delivery.
- a. Conducted for critical and high-value materials.
- b. Evaluates supplier quality control processes, production capabilities, and compliance.
- c. Findings are reported, and corrective actions are requested if deficiencies are found.
11. Work Hand-off
A structured process for transferring completed work between teams or subcontractors.
- a. Includes inspection checklists and approval documents.
- b. Ensures that quality standards are met before proceeding to the next stage.
- c. Reduces rework and prevents defects from carrying forward.
12. Snagging
A process to identify and rectify defects before project handover.
- a. Snag lists are prepared during final inspections.
- b. Defective works are documented and assigned for correction.
- c. Follow-up inspections ensure completion of all corrective actions before handover.
13. Internal Quality Audits
Regular assessments to ensure compliance with QA/QC standards and procedures.
- a. Conducted by internal auditors on a scheduled or surprise basis.
- b. Evaluate documentation, process adherence, and quality control effectiveness.
- c. Findings are reported to management, with corrective action plans assigned.
14. Risk and Opportunity Management
A proactive approach to identifying quality risks and potential improvements.
- a. Risk assessments are conducted at the planning stage and periodically updated.
- b. Mitigation plans are developed for high-risk areas.
- c. Opportunities for innovation and process enhancement are identified and implemented.
15. Project Score Card
Utilized to assess project performance, individual engineer performance, and other key metrics.
- a. The project score is computed based on quality, safety, engineering submittals, lean and Kaizen implementation.
- b. The project score is reported every month.
By implementing these processes, ECC ensures a structured, proactive, and continuous improvement-driven approach to quality management, leading to enhanced project outcomes and customer satisfaction.
ECC’s Quality Assurance (QA) and Quality Control (QC) Strategy
The Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC) strategy adopted by ECC is a comprehensive and structured approach designed to ensure excellence in all aspects of operations. This strategy is built upon several key pillars that foster a culture of continuous improvement, collaboration, and operational efficiency.
- Knowledge Sharing – ECC believes that quality is driven by collective expertise. By encouraging open communication and the exchange of best practices, the organization ensures that valuable insights, lessons learned, and technical know-how are disseminated across teams. This approach enhances problem-solving capabilities and promotes a proactive mindset toward quality.
- Empowerment – Employees are given the tools, authority, and confidence to make decisions that contribute to quality improvement. Through structured delegation, employees at all levels are encouraged to take ownership of quality-related tasks, driving accountability and fostering a sense of responsibility.
- “You Grow, We Grow” Philosophy – ECC recognizes that organizational success is directly linked to the growth and development of its employees. By investing in their professional and technical skills, the company ensures that as individuals progress in their careers, the overall quality of work also improves.
- Training and Personnel Development – Continuous learning is a cornerstone of ECC’s QA/QC strategy. Employees undergo regular training programs tailored to enhance their technical expertise, problem-solving abilities, and understanding of quality standards. This ensures that they remain up to date with industry advancements and best practices.
- Data-Driven Decision Making – ECC leverages data analytics to drive quality improvements. By collecting, analyzing, and interpreting key performance indicators (KPIs) and quality-related metrics, informed decisions are made to optimize processes and reduce defects.
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and Performance Monitoring – Performance metrics are established to track quality levels, identify trends, and measure improvements over time. Regular monitoring and reporting ensure that quality objectives are met, and any deviations are promptly addressed through corrective actions.
- Systemization of Processes – Standardized procedures and structured workflows are implemented to ensure consistency and efficiency. Well-documented quality management systems (QMS) help maintain uniformity across projects, minimizing variations, and ensuring compliance with industry standards.
- Embedding Quality Within the Process – Rather than treating quality as an afterthought or a final inspection step, ECC integrates quality principles throughout every phase of operations. By designing quality into processes from the outset, potential issues are identified and mitigated early, reducing rework and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Building Quality into the Process – ECC prioritizes a proactive approach to quality assurance by focusing on preventive measures rather than reactive corrections. By embedding quality checkpoints within workflows and fostering a quality-conscious work culture, the organization ensures that quality is maintained consistently across all projects.
This holistic QA/QC strategy aligns ECC’s quality objectives with its operational goals, ensuring sustainable growth, customer satisfaction, and industry leadership.
ECC’s Commitment to QA/QC Excellence
ECC is dedicated to maintaining the highest standards of quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) across its projects. Through the adoption of cutting-edge digital tools, online portals, and smart devices, ECC has significantly enhanced the efficiency, accuracy, and sustainability of its QA/QC processes.
One of the key achievements of ECC’s QA/QC initiatives is the reduction of paperwork by transitioning to a fully digital system. By utilizing online portals and mobile tablets for inspections and record-keeping, ECC has successfully eliminated the need for paper-based documentation, aligning with its commitment to achieving a paperless work environment.
The digitization of QA/QC processes has streamlined various critical functions, including:
- Inspections: Digital checklists and automated reporting ensure a more systematic and error-free inspection process.
- Non-Conformance Management: Online tracking and resolution of non-conformance issues allow for quicker corrective actions, reducing project delays.
- Snagging Process: Digital tools facilitate the efficient identification, reporting, and resolution of snags, improving project delivery timelines.
- Inspection Checklists: The use of standardized digital checklists enhances consistency and compliance across all projects.
By integrating digital solutions into QA/QC operations, ECC has not only increased efficiency and accuracy but has also optimized manpower utilization and enhanced real-time reporting capabilities. This transformation underscores ECC’s commitment to continuous improvement, sustainability, and operational excellence in the construction industry.
Proven Track Record of Timely Project Completion
In 2024, ECC successfully delivered several major projects on schedule, further solidifying its reputation for excellence in project execution, such as:
- Creek Beach Phase 3 was completed two months ahead of schedule, demonstrating ECC’s ability to accelerate project timelines without compromising quality.
- Phases 4 & 5 were finished 25 days earlier than planned, reflecting the efficiency and effectiveness of ECC’s streamlined processes.
These achievements highlight ECC’s commitment to exceeding client expectations and ensuring timely project delivery, reinforcing its position as a leader in the construction industry.
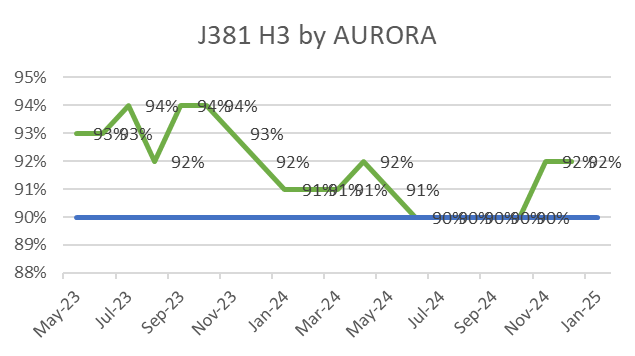
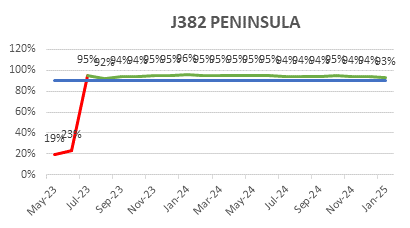
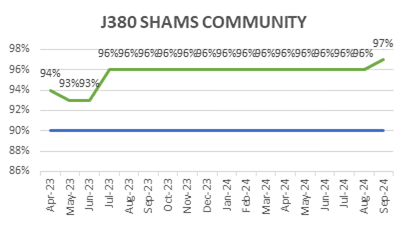
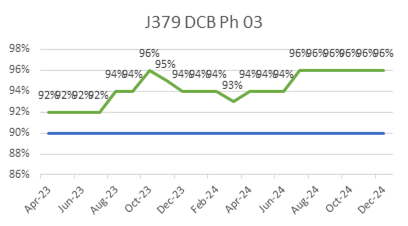
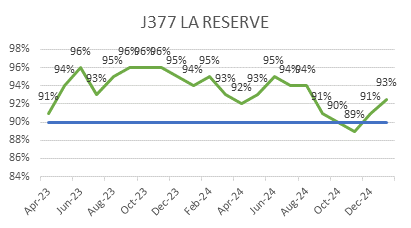
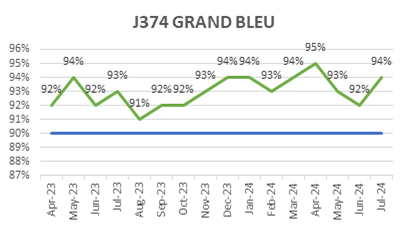
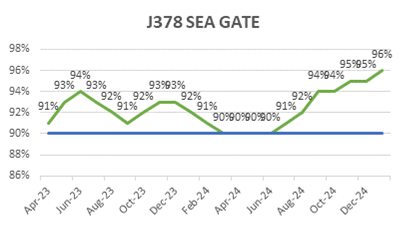
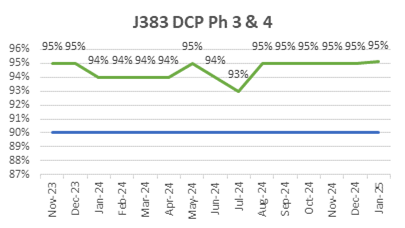
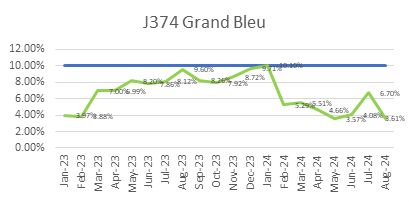
ECC’s focus on quality is reflected in its consistently low WIR Rejection Rates (Target <10%), as shown below, ensuring projects meet both timelines and standards.
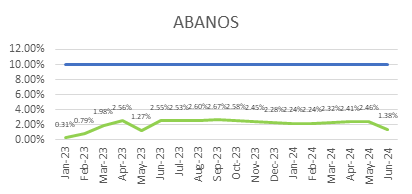
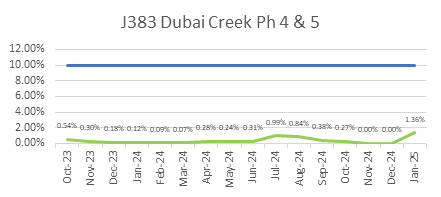
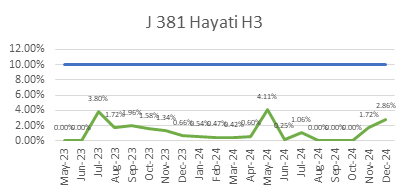
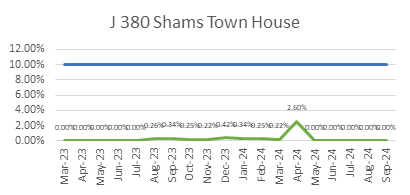
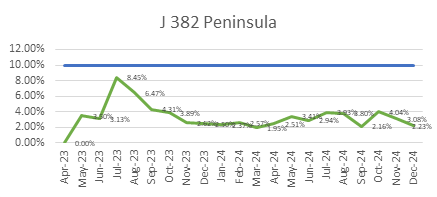
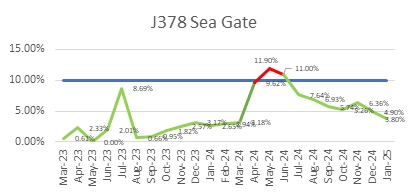
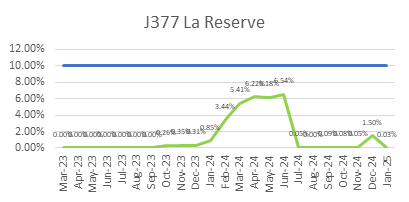
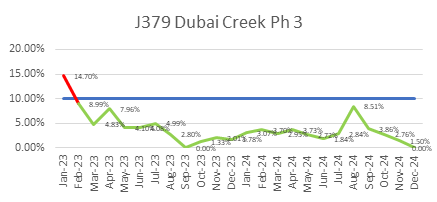
ECC’s Vision for Continuous Quality Improvement
At ECC, quality is not just a checkpoint but the foundation of everything we do. We integrate quality into every process, proactively refining operations to prevent defects, minimize risks, and enhance efficiency. By empowering our people through training and accountability, leveraging real-time data for informed decision-making, and standardizing best practices, we ensure consistency and excellence across all projects. Our commitment to continuous innovation and stakeholder satisfaction drives us to adopt cutting-edge technologies and industry-leading methodologies, positioning ECC as a benchmark for quality excellence, sustainable growth, and long-term reliability.
